Is the construction industry up to the challenge of repairing the world’s crumbling infrastructure? A new report from McKinsey & Co. answers with a definitive “No,” unless the industry can place itself firmly into the digital future in its organization, documentation, management, and information sharing.
The think tank estimates that the world will need to spend $57 trillion on infrastructure by 2030 just to keep pace with global economic growth. A recent report by three of its researchers also sees a construction industry that takes 20% longer than scheduled to finish most projects that come in up to 80% over budget.
“Construction productivity has actually declined in some markets since the 1990s,” writes the report’s authors, Rajat Agarwal, Shankar Chandrasekaran, and Mukund Srishar, in an article they posted last month. “The construction industry is ripe for disruption.”
Such observations are hardly new; there have been myriad other reports that lament the same problems in the construction sector, and fret about how massive reconstruction can possibly be accomplished.
What makes this paper a little different is that the “five big ideas” proposed by its authors aren’t at all futuristic.
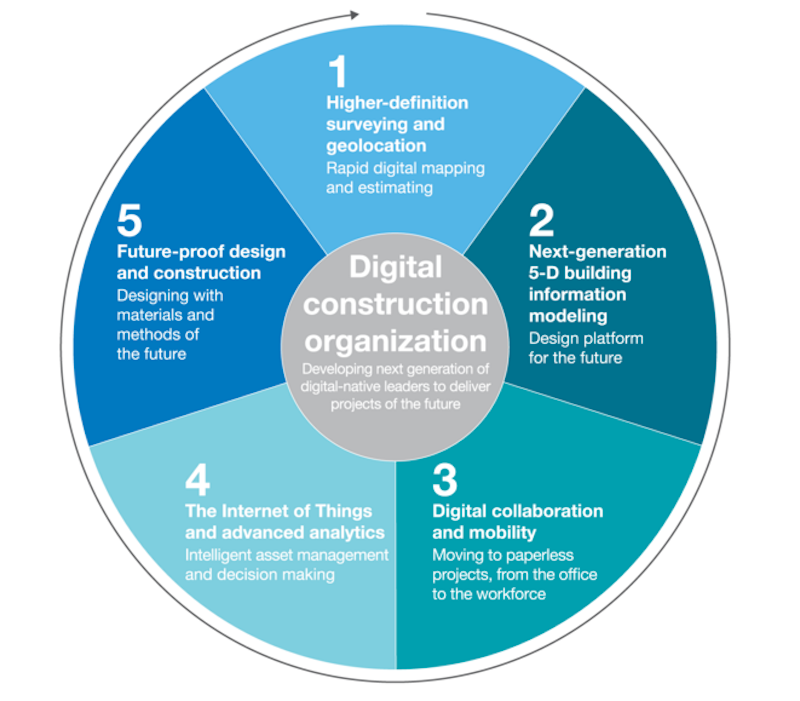
Five trends that are making the construction process run smoother and quicker. Image: McKinsey & Co.
The authors basically believe that the construction industry needs to be reorganized around digital technology, including:
•Higher-definition surveying and geolocation
•Next-generation 5D BIM
•Digital collaboration and mobility
•The Internet of Things (IoT), coupled with advanced analytics
•Future-proof design and construction with sustainable materials and methods.
Within these trends, McKinsey sees LIDAR as “an evolution in surveying,” primarily because of breakthroughs in drone technology and handheld platforms.
Five-D BIM goes beyond 3D BIM by taking into account a project’s cost and schedule. “The visual and intuitive nature of 5D BIM gives contractors a better chance to identify risk earlier, and thus to make better decisions.” Augmented reality technology will further enhance the effectiveness of 5D BIM, which project owners and contractors “need to incorporate right from the design stage.”
McKinsey revisits the need for the construction sector to move aggressively toward online communication as a way of improving productivity. Paper, the report argues, makes data analysis among team members tougher, and is subject to being mismanaged among different stakeholders.
By comparison, the authors point to an American tunnel project that involved 600 vendors, for which the contractor developed a single platform for bidding, tendering, and contract management. “This saved the team more than 20 hours of staff time per week, and cut down the time to generate reports by 75%,” they write.
Perhaps more to the point, the digital-collaboration and mobility solutions segments have attracted close to 60% of all venture capital funding in the construction-technology sector.
The report also suggests several advantageous potential uses for IoT working in combination with sensors and near-field-communication devices. These uses include equipment monitoring and repair, inventory management and ordering, quality assessment, energy efficiency (such as sensors monitoring ambient conditions and fuel consumption of equipment), and safety.
As for future proofing projects, the report lists a host of new building materials—self-healing concrete, aerogels, nanomaterials—and construction approaches—like 3D printing and preassembled modules—that could lower cost and speed up the construction process.
“Some of these ‘materials of the future’ could redefine how projects are conceptualized, designed, and executed,” states the report. It notes, however, that adoption of these materials has been slowed by a lack of awareness and availability, limited supply chain, and the industry’s risk aversion.
While 80% of all construction work is still done on-site, more project developers and contractors are deploying off-site approaches “that help them improve predictability, consistency, and repeatability.” These approaches include preassembly of components and simply structures, 3D printing, and robot-assembled construction.
None of these recommendations will surprise any nonresidential contractor. The question, though, is why aren’t these ideas being implemented more widely? The McKinsey authors say the industry needs “to adopt a new mindset” whose foundation is shared responsibility, and has four principles:
•Transparency and risk sharing in contracts
•Return-on-investment orientation
•Simplicity and intuitiveness in the design of new solutions
•Change management (as in top management communicating clearly why changes are important)
Project owners and developers need to mandate the adoption of digital technologies and measure results. This should include appointing a Chief Technology Officer or Chief Innovation Officer who can think boldly about the company’s digital agenda.
Engineers and contractors need to develop “digital road maps” for project management. “And it’s important to ensure that project teams have the budgets and authority they need to pilot new technologies. It’s essential to build the capabilities of project managers so they can become digitally adept.”
Related Stories
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Jun 22, 2023
NFL's Jacksonville Jaguars release conceptual designs for ‘stadium of the future’
Designed by HOK, the Stadium of the Future intends to meet the evolving needs of all stadium stakeholders—which include the Jaguars, the annual Florida-Georgia college football game, the TaxSlayer.com Gator Bowl, international sporting events, music festivals and tours, and the thousands of fans and guests who attend each event.
Contractors | Jun 22, 2023
Chris Averill named President of Pepper Construction Group
Pepper Construction Group is pleased to announced the promotion of Chris Averill to the position of President. In his new role, Averill will assume leadership responsibility for the Pepper Construction Group’s growth and performance.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 20, 2023
A new study presses for measuring embodied carbon in industrial buildings
The embodied carbon (EC) intensity in core and shell industrial buildings in the U.S. averages 23.0 kilograms per sf, according to a recent analysis of 26 whole building life-cycle assessments. That means a 300,000-sf warehouse would emit 6,890 megatons of carbon over its lifespan, or the equivalent of the carbon emitted by 1,530 gas-powered cars driven for one year. Those sobering estimates come from a new benchmark study, “Embodied Carbon U.S. Industrial Real Estate.”
Virtual Reality | Jun 16, 2023
Can a VR-enabled AEC Firm transform building projects?
With the aid of virtual reality and 3D visualization technologies, designers, consultants, and their clients can envision a place as though the project were in a later stage.
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
AEC Innovators | Jun 15, 2023
Rogers-O'Brien Construction pilots wearables to reduce heat-related injuries on jobsites
Rogers-O'Brien Construction (RO) has launched a pilot program utilizing SafeGuard, a safety-as-a-service platform for real-time health and safety risk assessment. Non-invasive wearables connected to SafeGuard continuously monitor personnel to prevent heat exhaustion on jobsites, reducing the risk of related injuries. RO is the first general contractor to pilot this program.
Office Buildings | Jun 15, 2023
An office building near DFW Airport is now home to two Alphabet companies
A five-minute drive from the Dallas-Fort Worth International Airport, the recently built 2999 Olympus is now home to two Alphabet companies: Verily, a life sciences business, and Wing, a drone delivery company. Verily and Wing occupy the top floor (32,000 sf and 4,000 sf, respectively) of the 10-story building, located in the lakeside, work-life-play development of Cypress Waters.
Transit Facilities | Jun 15, 2023
Arlington, Va., transit station will support zero emissions bus fleet
Arlington (Va.) Transit’s new operations and maintenance facility will support a transition of their current bus fleet to Zero Emissions Buses (ZEBs). The facility will reflect a modern industrial design with operational layouts to embrace a functional aesthetic. Intuitive entry points and wayfinding will include biophilic accents.
Urban Planning | Jun 15, 2023
Arizona limits housing projects in Phoenix area over groundwater supply concerns
Arizona will no longer grant certifications for new residential developments in Phoenix, it’s largest city, due to concerns over groundwater supply. The announcement indicates that the Phoenix area, currently the nation’s fastest-growing region in terms of population growth, will not be able to sustain its rapid growth because of limited freshwater resources.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 15, 2023
Alliance of Pittsburgh building owners slashes carbon emissions by 45%
The Pittsburgh 2030 District, an alliance of property owners in the Pittsburgh area, says that it has reduced carbon emissions by 44.8% below baseline. Begun in 2012 under the guidance of the Green Building Alliance (GBA), the Pittsburgh 2030 District encompasses more than 86 million sf of space within 556 buildings.

















