Is the construction industry up to the challenge of repairing the world’s crumbling infrastructure? A new report from McKinsey & Co. answers with a definitive “No,” unless the industry can place itself firmly into the digital future in its organization, documentation, management, and information sharing.
The think tank estimates that the world will need to spend $57 trillion on infrastructure by 2030 just to keep pace with global economic growth. A recent report by three of its researchers also sees a construction industry that takes 20% longer than scheduled to finish most projects that come in up to 80% over budget.
“Construction productivity has actually declined in some markets since the 1990s,” writes the report’s authors, Rajat Agarwal, Shankar Chandrasekaran, and Mukund Srishar, in an article they posted last month. “The construction industry is ripe for disruption.”
Such observations are hardly new; there have been myriad other reports that lament the same problems in the construction sector, and fret about how massive reconstruction can possibly be accomplished.
What makes this paper a little different is that the “five big ideas” proposed by its authors aren’t at all futuristic.
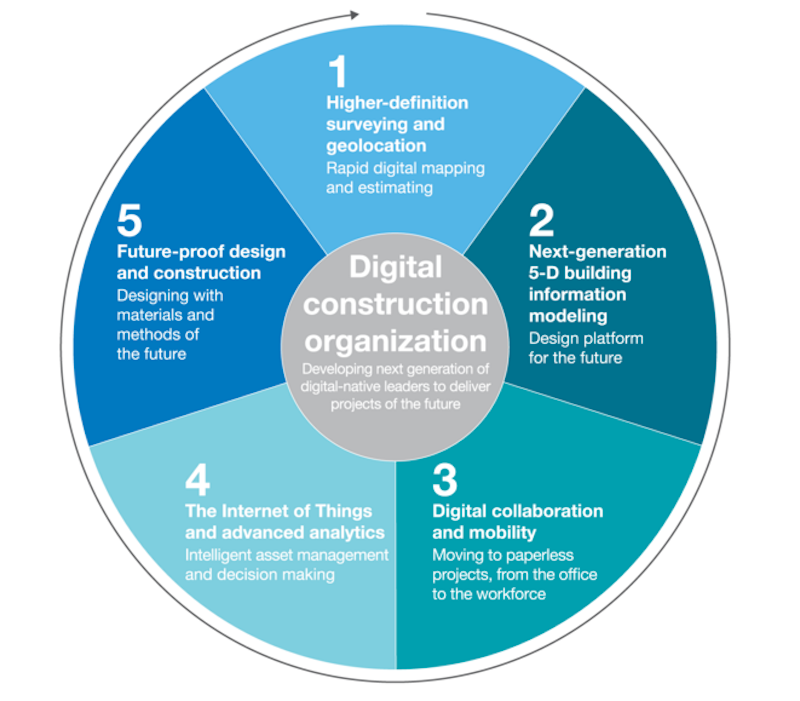
Five trends that are making the construction process run smoother and quicker. Image: McKinsey & Co.
The authors basically believe that the construction industry needs to be reorganized around digital technology, including:
•Higher-definition surveying and geolocation
•Next-generation 5D BIM
•Digital collaboration and mobility
•The Internet of Things (IoT), coupled with advanced analytics
•Future-proof design and construction with sustainable materials and methods.
Within these trends, McKinsey sees LIDAR as “an evolution in surveying,” primarily because of breakthroughs in drone technology and handheld platforms.
Five-D BIM goes beyond 3D BIM by taking into account a project’s cost and schedule. “The visual and intuitive nature of 5D BIM gives contractors a better chance to identify risk earlier, and thus to make better decisions.” Augmented reality technology will further enhance the effectiveness of 5D BIM, which project owners and contractors “need to incorporate right from the design stage.”
McKinsey revisits the need for the construction sector to move aggressively toward online communication as a way of improving productivity. Paper, the report argues, makes data analysis among team members tougher, and is subject to being mismanaged among different stakeholders.
By comparison, the authors point to an American tunnel project that involved 600 vendors, for which the contractor developed a single platform for bidding, tendering, and contract management. “This saved the team more than 20 hours of staff time per week, and cut down the time to generate reports by 75%,” they write.
Perhaps more to the point, the digital-collaboration and mobility solutions segments have attracted close to 60% of all venture capital funding in the construction-technology sector.
The report also suggests several advantageous potential uses for IoT working in combination with sensors and near-field-communication devices. These uses include equipment monitoring and repair, inventory management and ordering, quality assessment, energy efficiency (such as sensors monitoring ambient conditions and fuel consumption of equipment), and safety.
As for future proofing projects, the report lists a host of new building materials—self-healing concrete, aerogels, nanomaterials—and construction approaches—like 3D printing and preassembled modules—that could lower cost and speed up the construction process.
“Some of these ‘materials of the future’ could redefine how projects are conceptualized, designed, and executed,” states the report. It notes, however, that adoption of these materials has been slowed by a lack of awareness and availability, limited supply chain, and the industry’s risk aversion.
While 80% of all construction work is still done on-site, more project developers and contractors are deploying off-site approaches “that help them improve predictability, consistency, and repeatability.” These approaches include preassembly of components and simply structures, 3D printing, and robot-assembled construction.
None of these recommendations will surprise any nonresidential contractor. The question, though, is why aren’t these ideas being implemented more widely? The McKinsey authors say the industry needs “to adopt a new mindset” whose foundation is shared responsibility, and has four principles:
•Transparency and risk sharing in contracts
•Return-on-investment orientation
•Simplicity and intuitiveness in the design of new solutions
•Change management (as in top management communicating clearly why changes are important)
Project owners and developers need to mandate the adoption of digital technologies and measure results. This should include appointing a Chief Technology Officer or Chief Innovation Officer who can think boldly about the company’s digital agenda.
Engineers and contractors need to develop “digital road maps” for project management. “And it’s important to ensure that project teams have the budgets and authority they need to pilot new technologies. It’s essential to build the capabilities of project managers so they can become digitally adept.”
Related Stories
| Feb 11, 2011
Four Products That Stand Up to Hurricanes
What do a panelized wall system, a newly developed roof hatch, spray polyurethane foam, and a custom-made curtain wall have in common? They’ve been extensively researched and tested for their ability to take abuse from the likes of Hurricane Katrina.
| Feb 11, 2011
RS Means Cost Comparison Chart: Office Buildings
This month's RS Means Cost Comparison Chart focuses on office building construction.
| Feb 11, 2011
Sustainable features on the bill for dual-building performing arts center at Soka University of America
The $73 million Soka University of America’s new performing arts center and academic complex recently opened on the school’s Aliso Viejo, Calif., campus. McCarthy Building Companies and Zimmer Gunsul Frasca Architects collaborated on the two-building project. One is a three-story, 47,836-sf facility with a grand reception lobby, a 1,200-seat auditorium, and supports spaces. The other is a four-story, 48,974-sf facility with 11 classrooms, 29 faculty offices, a 150-seat black box theater, rehearsal/dance studio, and support spaces. The project, which has a green roof, solar panels, operable windows, and sun-shading devices, is going for LEED Silver.
| Feb 11, 2011
BIM-enabled Texas church complex can broadcast services in high-def
After two years of design and construction, members of the Gateway Church in Southland, Texas, were able to attend services in their new 4,000-seat facility in late 2010. Located on a 180-acre site, the 205,000-sf complex has six auditoriums, including a massive 200,000-sf Worship Center, complete with catwalks, top-end audio and video system, and high-definition broadcast capabilities. BIM played a significant role in the building’s design and construction. Balfour Beatty Construction and Beck Architecture formed the nucleus of the Building Team.
| Feb 11, 2011
Kentucky’s first green adaptive reuse project earns Platinum
(FER) studio, Inglewood, Calif., converted a 115-year-old former dry goods store in Louisville, Ky., into a 10,175-sf mixed-use commercial building earned LEED Platinum and holds the distinction of being the state’s first adaptive reuse project to earn any LEED rating. The facility, located in the East Market District, houses a gallery, event space, offices, conference space, and a restaurant. Sustainable elements that helped the building reach its top LEED rating include xeriscaping, a green roof, rainwater collection and reuse, 12 geothermal wells, 81 solar panels, a 1,100-gallon ice storage system (off-grid energy efficiency is 68%) and the reuse and recycling of construction materials. Local firm Peters Construction served as GC.
| Feb 11, 2011
Former Richardson Romanesque hotel now houses books, not beds
The Piqua (Ohio) Public Library was once a late 19th-century hotel that sat vacant and deteriorating for years before a $12.3 million adaptive reuse project revitalized the 1891 building. The design team of PSA-Dewberry, MKC Associates, and historic preservation specialist Jeff Wray Associates collaborated on the restoration of the 80,000-sf Richardson Romanesque building, once known as the Fort Piqua Hotel. The team restored a mezzanine above the lobby and repaired historic windows, skylight, massive fireplace, and other historic details. The basement, with its low ceiling and stacked stone walls, was turned into a castle-like children’s center. The Piqua Historical Museum is also located within the building.
| Feb 11, 2011
Justice center on Fall River harbor serves up daylight, sustainable elements, including eucalyptus millwork
Located on historic South Main Street in Fall River, Mass., the Fall River Justice Center opened last fall to serve as the city’s Superior and District Courts building. The $85 million facility was designed by Boston-based Finegold Alexander + Associates Inc., with Dimeo Construction as CM and Arup as MEP. The 154,000-sf courthouse contains nine courtrooms, a law library, and a detention area. Most of the floors have the same ceiling height, which will makes them easier to reconfigure in the future as space needs change. Designed to achieve LEED Silver, the facility’s elliptical design offers abundant natural daylight and views of the harbor. Renewable eucalyptus millwork is one of the sustainable features.
| Feb 11, 2011
Research facility separates but also connects lab spaces
California State University, Northridge, consolidated its graduate and undergraduate biology and mathematics programs into one 90,000-sf research facility. Architect of record Cannon Design worked on the new Chaparral Hall, creating a four-story facility with two distinct spaces that separate research and teaching areas; these are linked by faculty offices to create collaborative spaces. The building houses wet research, teaching, and computational research labs, a 5,000-sf vivarium, classrooms, and administrative offices. A four-story outdoor lobby and plaza and an outdoor staircase provide orientation. A covered walkway links the new facility with the existing science complex. Saiful/Bouquet served as structural engineer, Bard, Rao + Athanas Consulting Engineers served as MEP, and Research Facilities Design was laboratory consultant.
| Feb 11, 2011
A feast of dining options at University of Colorado community center, but hold the buffalo stew
The University of Colorado, Boulder, cooked up something different with its new $84.4 million Center for Community building, whose 900-seat foodservice area consists of 12 micro-restaurants, each with its own food options and décor. Centerbrook Architects of Connecticut collaborated with Denver’s Davis Partnership Architects and foodservice designer Baker Group of Grand Rapids, Mich., on the 323,000-sf facility, which also includes space for a career center, international education, and counseling and psychological services. Exterior walls of rough-hewn, variegated sandstone and a terra cotta roof help the new facility blend with existing campus buildings. Target: LEED Gold.
| Feb 11, 2011
Chicago high-rise mixes condos with classrooms for Art Institute students
The Legacy at Millennium Park is a 72-story, mixed-use complex that rises high above Chicago’s Michigan Avenue. The glass tower, designed by Solomon Cordwell Buenz, is mostly residential, but also includes 41,000 sf of classroom space for the School of the Art Institute of Chicago and another 7,400 sf of retail space. The building’s 355 one-, two-, three-, and four-bedroom condominiums range from 875 sf to 9,300 sf, and there are seven levels of parking. Sky patios on the 15th, 42nd, and 60th floors give owners outdoor access and views of Lake Michigan.
















