Is the construction industry up to the challenge of repairing the world’s crumbling infrastructure? A new report from McKinsey & Co. answers with a definitive “No,” unless the industry can place itself firmly into the digital future in its organization, documentation, management, and information sharing.
The think tank estimates that the world will need to spend $57 trillion on infrastructure by 2030 just to keep pace with global economic growth. A recent report by three of its researchers also sees a construction industry that takes 20% longer than scheduled to finish most projects that come in up to 80% over budget.
“Construction productivity has actually declined in some markets since the 1990s,” writes the report’s authors, Rajat Agarwal, Shankar Chandrasekaran, and Mukund Srishar, in an article they posted last month. “The construction industry is ripe for disruption.”
Such observations are hardly new; there have been myriad other reports that lament the same problems in the construction sector, and fret about how massive reconstruction can possibly be accomplished.
What makes this paper a little different is that the “five big ideas” proposed by its authors aren’t at all futuristic.
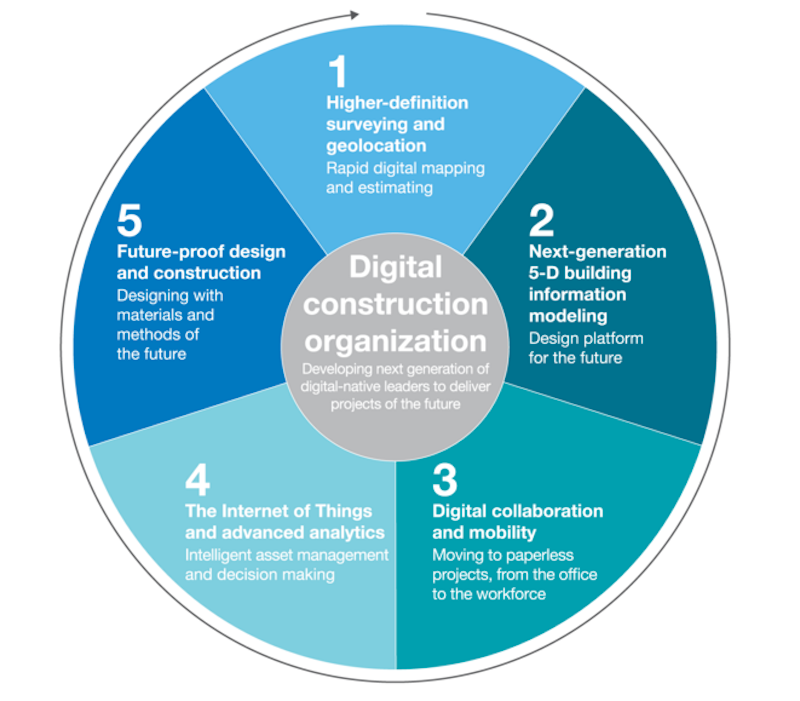
Five trends that are making the construction process run smoother and quicker. Image: McKinsey & Co.
The authors basically believe that the construction industry needs to be reorganized around digital technology, including:
•Higher-definition surveying and geolocation
•Next-generation 5D BIM
•Digital collaboration and mobility
•The Internet of Things (IoT), coupled with advanced analytics
•Future-proof design and construction with sustainable materials and methods.
Within these trends, McKinsey sees LIDAR as “an evolution in surveying,” primarily because of breakthroughs in drone technology and handheld platforms.
Five-D BIM goes beyond 3D BIM by taking into account a project’s cost and schedule. “The visual and intuitive nature of 5D BIM gives contractors a better chance to identify risk earlier, and thus to make better decisions.” Augmented reality technology will further enhance the effectiveness of 5D BIM, which project owners and contractors “need to incorporate right from the design stage.”
McKinsey revisits the need for the construction sector to move aggressively toward online communication as a way of improving productivity. Paper, the report argues, makes data analysis among team members tougher, and is subject to being mismanaged among different stakeholders.
By comparison, the authors point to an American tunnel project that involved 600 vendors, for which the contractor developed a single platform for bidding, tendering, and contract management. “This saved the team more than 20 hours of staff time per week, and cut down the time to generate reports by 75%,” they write.
Perhaps more to the point, the digital-collaboration and mobility solutions segments have attracted close to 60% of all venture capital funding in the construction-technology sector.
The report also suggests several advantageous potential uses for IoT working in combination with sensors and near-field-communication devices. These uses include equipment monitoring and repair, inventory management and ordering, quality assessment, energy efficiency (such as sensors monitoring ambient conditions and fuel consumption of equipment), and safety.
As for future proofing projects, the report lists a host of new building materials—self-healing concrete, aerogels, nanomaterials—and construction approaches—like 3D printing and preassembled modules—that could lower cost and speed up the construction process.
“Some of these ‘materials of the future’ could redefine how projects are conceptualized, designed, and executed,” states the report. It notes, however, that adoption of these materials has been slowed by a lack of awareness and availability, limited supply chain, and the industry’s risk aversion.
While 80% of all construction work is still done on-site, more project developers and contractors are deploying off-site approaches “that help them improve predictability, consistency, and repeatability.” These approaches include preassembly of components and simply structures, 3D printing, and robot-assembled construction.
None of these recommendations will surprise any nonresidential contractor. The question, though, is why aren’t these ideas being implemented more widely? The McKinsey authors say the industry needs “to adopt a new mindset” whose foundation is shared responsibility, and has four principles:
•Transparency and risk sharing in contracts
•Return-on-investment orientation
•Simplicity and intuitiveness in the design of new solutions
•Change management (as in top management communicating clearly why changes are important)
Project owners and developers need to mandate the adoption of digital technologies and measure results. This should include appointing a Chief Technology Officer or Chief Innovation Officer who can think boldly about the company’s digital agenda.
Engineers and contractors need to develop “digital road maps” for project management. “And it’s important to ensure that project teams have the budgets and authority they need to pilot new technologies. It’s essential to build the capabilities of project managers so they can become digitally adept.”
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
Lab personnel find comfort in former Winchester gun factory
The former Winchester Repeating Arms Factory in New Haven, Conn., is the new home of PepsiCo’s Biology Innovation Research Laboratory.
| May 18, 2011
Addition provides new school for pre-K and special-needs kids outside Chicago
Perkins+Will, Chicago, designed the Early Learning Center, a $9 million, 37,000-sf addition to Barrington Middle School in Barrington, Ill., to create an easily accessible and safe learning environment for pre-kindergarten and special-needs students.
| May 18, 2011
Raphael Viñoly’s serpentine-shaped building snakes up San Francisco hillside
The hillside location for the Ray and Dagmar Dolby Regeneration Medicine building at the University of California, San Francisco, presented a challenge to the Building Team of Raphael Viñoly, SmithGroup, DPR Construction, and Forell/Elsesser Engineers. The 660-foot-long serpentine-shaped building sits on a structural framework 40 to 70 feet off the ground to accommodate the hillside’s steep 60-degree slope.
| May 18, 2011
New center provides home to medical specialties
Construction has begun on the 150,000-sf Medical Arts Pavilion at the University Medical Center in Princeton, N.J.
| May 18, 2011
Improvements add to Detroit convention center’s appeal
Interior and exterior renovations and updates will make the Detroit Cobo Center more appealing to conventioneers. A new 40,000-sf ballroom will take advantage of the center’s riverfront location, with views of the river and downtown.
| May 18, 2011
One of Delaware’s largest high schools seeks LEED for Schools designation
The $82 million, 280,000-sf Dover (Del.) High School will have capacity for 1,800 students and feature a 900-seat theater, a 2,500-seat gymnasium, and a 5,000-seat football stadium.
| May 18, 2011
Carnegie Hall vaults into the 21st century with a $200 million renovation
Historic Carnegie Hall in New York City is in the midst of a major $200 million renovation that will bring the building up to contemporary standards, increase educational and backstage space, and target LEED Silver.
| May 17, 2011
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 17, 2011
Gilbane partners with Steel Orca on ultra-green data center
Gilbane, along with Crabtree, Rohrbaugh & Associates, has been selected to partner with Steel Orca to design and build a 300,000-sf data center in Bucks County, Pa., that will be powered entirely through renewable energy sources--gas, solar, fuel cells, wind and geo-thermal. Completion is scheduled for 2013.
















