Experts, including those in the AEC community, who have been insisting for years that indoor air quality affects occupants’ performance and health could soon have more ammunition to back up their claims.
The Wall Street Journal reports that Washington University at St. Louis last summer initiated what will be a yearlong experiment to test whether a newly constructed building, designed with easy access to stairways, natural daylight, and other “wellness” features, improves employees’ physical well being and promotes worker collaboration. The Journal also reports that the Well Living Lab, a research facility near the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, early next year will begin clinical trials designed to assess indoor environments, with the goal of creating healthier spaces.
On October 26, Environmental Health Perspectives—a monthly journal of news and research published with support from the National Institute of Environmental Sciences (NIES), the National Institutes of Health, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services—released in advance of publication a peer-reviewed paper that details a recent study of 24 participants—architects, designers, programmers, engineers, creative marketers, and managers—who spent six full workdays in an environmentally controlled office space, blinded to test conditions.
The study population was restricted to non-sensitive persons by excluding current smokers and people with asthma, claustrophobia, or schizophrenia.
On different days, the participants were exposed to Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) conditions with high and low concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that were representative of office buildings in the U.S. Additional conditions simulated a Green building with a high outdoor air ventilation rate and artificially elevated carbon dioxide levels independent of ventilation.
The study found that, on average, the participants’ cognitive scores were 61% higher on Green building days and 101% higher on days when the air ventilation was highest (so-called Green+ days), compared to the air quality during “Conventional” building days. “These findings have wide-ranging implications because this study was designed to reflect conditions that are commonly encountered every day in many indoor environments,” the study’s authors state.
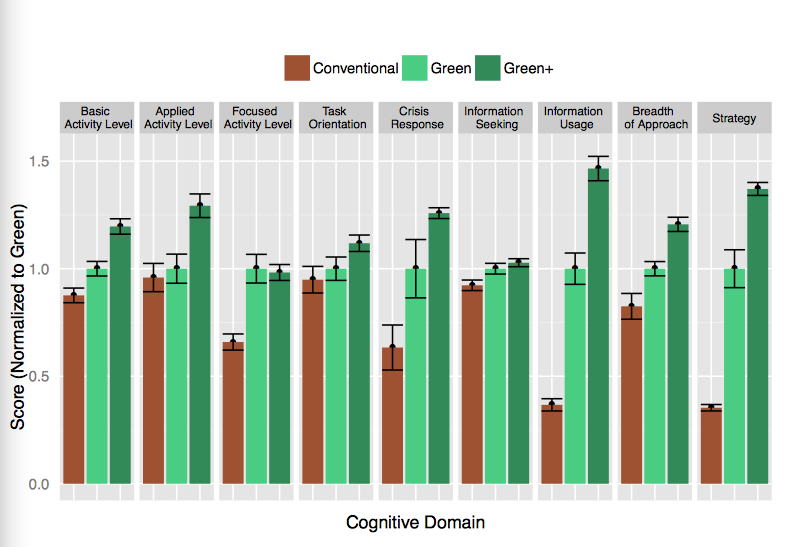 A recent study tested the cognition of 24 participants for nine activities, based on different levels of indoor air quality exposure. “Conventional” was air quality that's typical of most office buildings; Green+ indicated the highest level of air ventilation.
A recent study tested the cognition of 24 participants for nine activities, based on different levels of indoor air quality exposure. “Conventional” was air quality that's typical of most office buildings; Green+ indicated the highest level of air ventilation.
The study took place over two weeks in November 2014 at the Willis H. Carrier Total Indoor Environmental Quality Laboratory at the Syracuse Center for Excellence. The lab had two nearly identical office environments located adjacent to one another, each with 12 cubicles.
Cognitive assessment of the participants was performed daily using the Strategic Management Simulation software tool, a validated, computer-based test designed to test the effectiveness of management-level employees through assessments of higher-order decision-making.
The study found that the largest effects of conditions on cognition were seen for Crisis Response, Information Usage, and Strategy. For Crisis Response, for example, scores were 97% higher for the Green condition compared to the Conventional, and 131% higher for participants during Green+ days.
Conversely, “we found statistically significant declines in cognitive function scores when CO2 concentrations were increased to levels that are common in indoor spaces (approximately 950 ppm). In fact, this level of CO2 is considered acceptable because it would satisfy ASHRAE’s ventilation rate guideline for acceptable indoor air quality,” the authors state.
The paper, whose six authors worked under the auspices of NIES, was reviewed and approved by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Institutional Review Board. The participant group was 42% male, 58% female. One-third of the group was between the ages of 20 and 30, and 25% was between the ages of 41 and 50. Ninety-two percent of the group was Caucasian, 54% has a college degree, and 63% holds professional jobs.
Related Stories
| Mar 19, 2014
Is it time to start selecting your own clients?
Will 2014 be the year that design firms start selecting the clients they want rather than getting in line with competitors to respond to RFPs? That’s the question posed by a recent thought-provoking article.
| Mar 19, 2014
How to develop a healthcare capital project using a 'true north charter'
Because healthcare projects take years to implement, developing a true north charter is essential for keeping the entire team on track and moving in the right direction.
| Mar 18, 2014
6 keys to better healthcare design
Healthcare facility planning and design experts cite six factors that Building Teams need to keep in mind on their next healthcare project.
| Mar 18, 2014
Charles Dalluge joins DLR Group as president, COO
CEO Griff Davenport announces addition of Dalluge to executive leadership team
| Mar 13, 2014
Austria's tallest tower shimmers with striking 'folded façade' [slideshow]
The 58-story DC Tower 1 is the first of two high-rises designed by Dominique Perrault Architecture for Vienna's skyline.
| Mar 12, 2014
14 new ideas for doors and door hardware
From a high-tech classroom lockdown system to an impact-resistant wide-stile door line, BD+C editors present a collection of door and door hardware innovations.
| Mar 12, 2014
New CannonDesign database allows users to track facility assets
The new software identifies critical failures of components and systems, code and ADA-compliance issues, and systematically justifies prudent expenditures.
| Mar 11, 2014
Freelon Group to join Perkins+Will
The Freelon Group concentrates on museums, libraries, universities and other civic and institutional clients; Perkins+Will plans to incorporate this specialization into their design repertory.
| Mar 10, 2014
Meet Tally – the Revit app that calculates the environmental impact of building materials
Tally provides AEC professionals with insight into how materials-related decisions made during design influence a building’s overall ecological footprint.
| Mar 10, 2014
Field tested: Caterpillar’s Cat B15 rugged smartphone
The B15 is billed by Cat as “the most progressive, durable and rugged device available on the market today.”
















