Cities interested in bolstering their economies through innovation should look beyond the typical formalized processes.
Instead, a new paper from the Brookings Anne T. and Robert M. Bass Initiative on Innovation and Placemaking pushes economic development leaders to recognize that different types of firms innovate through distinct actors and both market and non-market channels. As a result, regions require industry-tailored innovation-support strategies.
In “How Firms Learn: Industry specific strategies for urban economies,” Brookings Senior Policy Analyst and Associate Fellow Scott Andes examines how manufacturing and software services firms develop new products, processes, and ideas. He illustrates three archetypal innovation models, which correspond to three industry types:
- Classic Industries, such as pharmaceuticals, work primarily with universities and other traditional innovation actors and use market channels, including contracts and licensing agreements, as sources of invention.
- Unconventional Industries, exemplified by small-and medium-sized manufacturers, primarily source innovation from clients and suppliers and pursue informal innovation channels, such as joint research agreements and supplier contracts.
- Mixed Industries predominantly rely on non-traditional actors but formal market channels to acquire innovation. Example industries include semiconductors, chemicals, and textiles.
“In order to build strong regional economies, urban economic development leaders should stop carbon copying other cities’ approaches and instead align local economic strategies with the particular ways their dominant industries innovate,” Andes said.
Specifically, public, private, and institutional stakeholders should develop strategies that:
- Recognize that all industries can be innovative, not just software and medical technology startups, and identify the particular innovation pathways utilized by local firms.
- Eliminate institution-wide technology transfer practices at research universities that focus on licensing and allow specific departments and centers to cater to different industries.
- Establish partnerships with non-research colleges and universities to support firms seeking short-term process innovation.
- Modify the traditional accelerator model to respond to the innovation needs of startups in nontraditional growth sectors.
- Link designers, engineers, and software developers in urban centers to manufacturing supply chains in the surrounding regions.
- Advance appropriate place-based strategies to increase the density of innovative firms and support organizations.
Such industry-contextualized approaches will allow for urban economic development resources to be used to their best advantage and firms and other innovation actors to maximize learning and economic power.
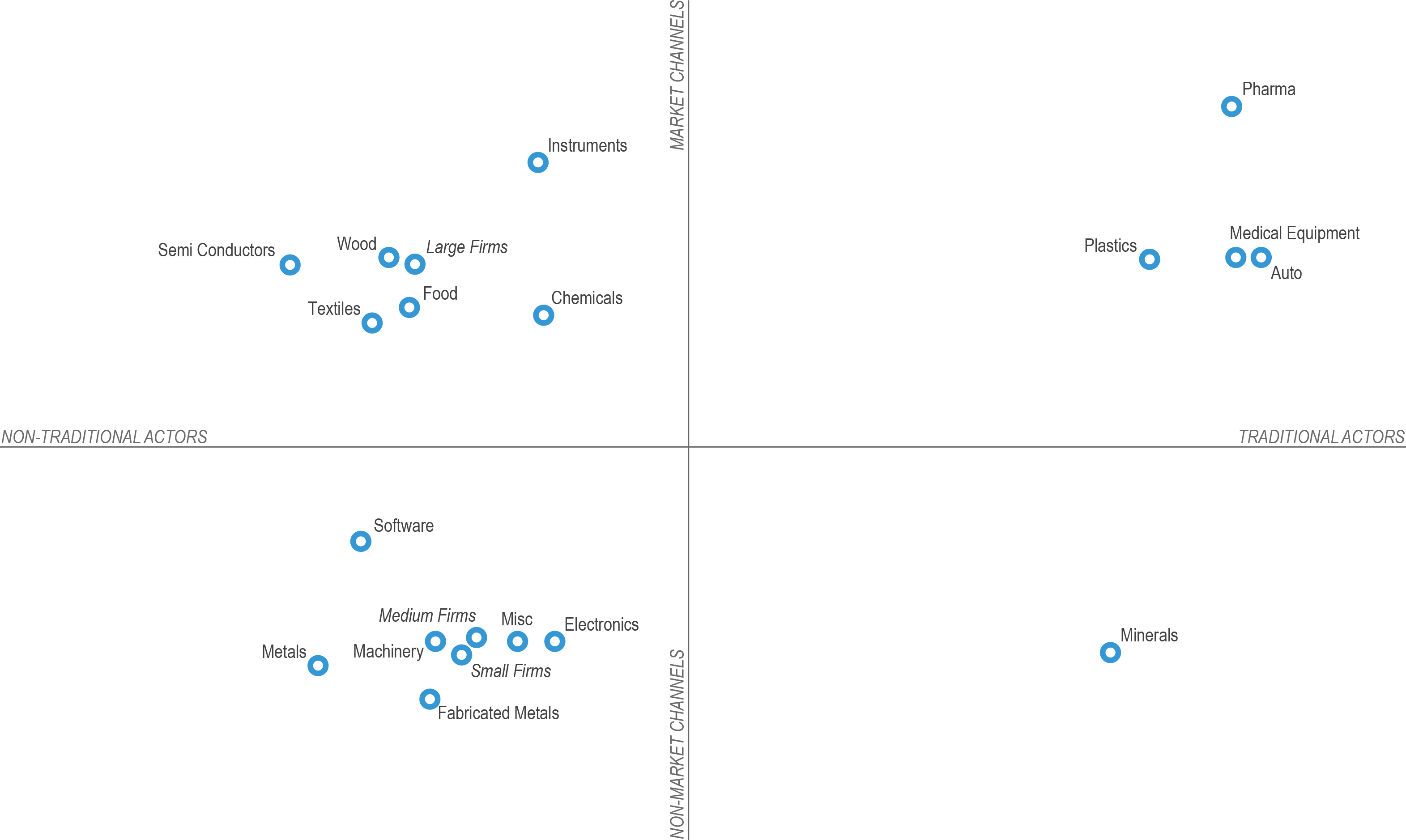 Sources of innovation and channels by which acquired, by industry. Source: Author’s analysis of Arora, Cohen, and Walsh (2014) and Graham (2009). Click image to enlarge.
Sources of innovation and channels by which acquired, by industry. Source: Author’s analysis of Arora, Cohen, and Walsh (2014) and Graham (2009). Click image to enlarge.
Related Stories
Sustainable Development | Jul 14, 2022
Designing for climate change and inclusion, with CBT Architects' Kishore Varanasi and Devanshi Purohit
Climate change is having a dramatic impact on urban design, in terms of planning, materials, occupant use, location, and the long-term effect of buildings on the environment. Joining BD+C's John Caulfield to discuss this topic are two experts from the Boston-based CBT Architects: Kishore Varanasi, a Principal and director of urban design; and Devanshi Purohit, an Associate Principal.
Sponsored | Healthcare Facilities | May 3, 2022
Planning for hospital campus access that works for people
This course defines the elements of hospital campus access that are essential to promoting the efficient, stress-free movement of patients, staff, family, and visitors. Campus access elements include signage and wayfinding, parking facilities, transportation demand management, shuttle buses, curb access, valet parking management, roadways, and pedestrian walkways.
Urban Planning | Apr 5, 2022
The art of master planning, with Mike Aziz of Cooper Robertson
Mike Aziz, AIA, LEED AP, Partner and Director of Urban Design with Cooper Robertson, discusses his firm's design for the redevelopment of a Connecticut town's riverfront.
Multifamily Housing | Mar 29, 2022
Here’s why the U.S. needs more ‘TOD’ housing
Transit-oriented developments help address the housing affordability issue that many cities and suburbs are facing.
Urban Planning | Feb 14, 2022
5 steps to remake suburbs into green communities where people want to live, work, and play
Stantec's John Bachmann offers proven tactic for retrofitting communities for success in the post-COVID era.
Urban Planning | Feb 11, 2022
6 ways to breathe life into mixed-use spaces
To activate mixed-use spaces and realize their fullest potential, project teams should aim to create a sense of community and pay homage to the local history.
Urban Planning | Jan 25, 2022
Retooling innovation districts for medium-sized cities
This type of development isn’t just about innovation or lab space; and it’s not just universities or research institutions that are driving this change.
Urban Planning | Dec 15, 2021
EV is the bridge to transit’s AV revolution—and now is the time to start building it
Thinking holistically about a technology-enabled customer experience will make transit a mode of choice for more people.
Designers / Specifiers / Landscape Architects | Nov 16, 2021
‘Desire paths’ and college campus design
If a campus is not as efficient as it could be, end users will use their feet to let designers know about it.
Urban Planning | Nov 11, 2021
Reimagining the concrete and steel jungle, SOM sees buildings that absorb more carbon than they emit
The firm presented its case for a cleaner built environment during the Climate Change conference in Scotland.

















