Next month, Amazon.com is scheduled to open the first phase of its massive Denny Triangle campus in Seattle. Through a unique partnership, the spheres and towers that comprise Amazon’s four-block, 4-million-sf campus will be heated by waste heat recovered from the 34-story Westin Building Exchange across the street.
The Seattle Times reports that 70% of the Westin Building Exchange’s 400,000 sf is dedicated to data centers that are throwing off tremendous amounts of excess heat.
The building produces heat equivalent to 11 megawatts per day. Through an agreement with Pacific Northwest, which routes nearly all of its Internet traffic through the data centers in Westin, the building will transfer up to five megawatts to Amazon, which is purchasing the energy at a discounted rate. Recapturing this waste heat is expected to save about 4 million kilowatt-hours of energy per year.
Here’s how this system will work, according to the Times and the Seattle Post-Intelligencer: When the Amazon buildings need heat, that will signal two heat pumps that collect heat from the data centers in the Westin Building Exchange, and use it to heat water traveling via pipes from the roof of the Westin building and through its floors to a refrigerator-sized steel-plated heat exchanger in Westin’s basement.
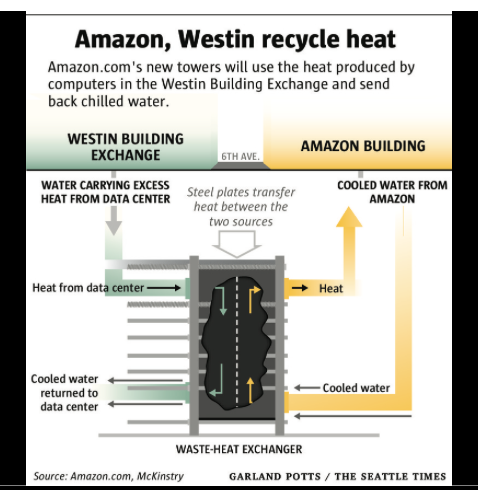 Image courtesy Amazon.com and McKinstry.
Image courtesy Amazon.com and McKinstry.
By the time that water reaches the exchanger, its temperature exceeds 70 degrees Fahrenheit. The exchanger transfers that heat through pipes running under the street to Amazon’s campus, which returns cooler water via the exchanger to the data centers.
When this system is fully functional, it will be circulating up to 3,000 gallons of water per minute.
Several entities collaborated on this project, which has been in the works for three years. They include McKinstry, which designed the heat-exchange system; and Clise Development, which co-owns the Westin Building Exchange with Digital Realty Trust, and sold Amazon the four blocks for its campus. Clise and McKinstry formed a partnership called Eco District for this project.
The agreement also involved several city agencies including its office of sustainability and environment. The Post-Intelligencer reports that one of Amazon’s building is already using this so-called district heating system that will ultimately provide heat for more than 3 million sf of office space.
Richard Stevenson, Clise Properties’ president, estimates the cost of this system in “the low millions” that would pay for itself in energy savings.
While heat exchange isn’t a new concept, it usually involves only one building, and rarely on the scale of this project. The Times quotes Susan Wickwire, executive director of the Seattle 2030 District—which aims to significantly reduce energy and water use in buildings in Seattle by 2030—who believes the arrangement between Amazon and Pacific Northwest could provide “a smooth path” for similar agreements where building occupants work together to save energy and make their operations more efficient.
“We’re showing people it can be done,” John Schoettler, Amazon’s director of global real estate, told the Times. “If other developments can model this, that’s a win-win.”
Amazon’s Denny Triangle campus, designed by NBBJ, will include three intersecting glass spheres that form a five-story office building, a 38-story tower, and 18,000 sf of retail. Amazon expects to be fully moved into these buildings in a couple of years.
Related Stories
| Dec 17, 2010
Alaskan village school gets a new home
Ayagina’ar Elitnaurvik, a new K-12 school serving the Lower Kuskikwim School District, is now open in Kongiganak, a remote Alaskan village of less than 400 residents. The 34,000-sf, 12-classroom facility replaces one that was threatened by river erosion.
| Dec 17, 2010
New engineering building goes for net-zero energy
A new $90 million, 250,000-sf classroom and laboratory facility with a 450-seat auditorium for the College of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana/Champaign is aiming for LEED Platinum.
| Dec 17, 2010
Vietnam business center will combine office and residential space
The 300,000-sm VietinBank Business Center in Hanoi, Vietnam, designed by Foster + Partners, will have two commercial towers: the first, a 68-story, 362-meter office tower for the international headquarters of VietinBank; the second, a five-star hotel, spa, and serviced apartments. A seven-story podium with conference facilities, retail space, restaurants, and rooftop garden will connect the two towers. Eco-friendly features include using recycled heat from the center’s power plant to provide hot water, and installing water features and plants to improve indoor air quality. Turner Construction Co. is the general contractor.
| Dec 13, 2010
Energy efficiency No. 1 priority for commercial office tenants
Green building initiatives are a key influencer when tenants decide to sign a commercial real estate lease, according to a survey by GE Capital Real Estate. The survey, which was conducted over the past year and included more than 2,220 office tenants in the U.S., Canada, France, Germany, Sweden, the UK, Spain, and Japan, shows that energy efficiency remains the No. 1 priority in most countries. Also ranking near the top: waste reduction programs and indoor air.
| Dec 7, 2010
USGBC: Wood-certification benchmarks fail to pass
The proposed Forest Certification Benchmark to determine when wood-certification groups would have their certification qualify for points in the LEED rating systemdid not pass the USGBC member ballot. As a result, the Certified Wood credit in LEED will remain as it is currently written. To date, only wood certified by the Forest Stewardship Council qualifies for a point in the LEED, while other organizations, such as the Sustainable Forestry Initiative, the Canadian Standards Association, and the American Tree Farm System, are excluded.
| Dec 6, 2010
Honeywell survey
Rising energy costs and a tough economic climate have forced the nation’s school districts to defer facility maintenance and delay construction projects, but they have also encouraged districts to pursue green initiatives, according to Honeywell’s second annual “School Energy and Environment Survey.”
| Dec 2, 2010
Alliance for Sustainable Built Environments adds Kohler's Robert Zimmerman to Board of Directors
Robert Zimmerman, Manager – Engineering, Water Conservation & Sustainability at Kohler Co., in Kohler, Wisconsin, has joined the Board of Directors of the Alliance for Sustainable Built Environments. In his position at Kohler Co., Rob is involved with all aspects of water conservation and sustainability related to plumbing fixtures and faucets.
| Dec 2, 2010
U.S Energy Secretary Chu announces $21 Million to improve energy use in commercial buildings
U.S. Energy Secretary Steven Chu announced that 24 projects are receiving a total of $21 million in technical assistance to dramatically reduce the energy used in their commercial buildings. This initiative will connect commercial building owners and operators with multidisciplinary teams including researchers at DOE's National Laboratories and private sector building experts. The teams will design, construct, measure, and test low-energy building plans, and will help accelerate the deployment of cost-effective energy-saving measures in commercial buildings across the United States.
| Nov 29, 2010
Data Centers: Keeping Energy, Security in Check
Power consumption for data centers doubled from 2000 and 2006, and it is anticipated to double again by 2011, making these mission-critical facilities the nation’s largest commercial user of electric power. Major technology companies, notably Hewlett-Packard, Cisco Systems, and International Business Machines, are investing heavily in new data centers. HP, which acquired technology services provider EDS in 2008, announced in June that it would be closing many of its older data centers and would be building new, more highly optimized centers around the world.











